Efficacy data

In the EFFISAYIL® 1 clinical trial, the Generalized Pustular Psoriasis Physician Global Assessment (GPPGA), which ranges from 0 (clear) to 4 (severe), was used to assess the efficacy of SPEVIGO® IV.
At Week 1, SPEVIGO® IV demonstrated efficacy in the primary and secondary endpoints vs. placebo:1*
GPPGA pustulation subscore of 0 (no visible pustules): 54.3% (n=19) vs. 5.6% (n=1) with placebo (p=0.0004†) (primary endpoint)
GPPGA total score of 0 or 1 (clear or almost clear skin): 42.9% (n=15) vs. 11.1% (n=2) with placebo (p=0.0118†) (secondary endpoint)
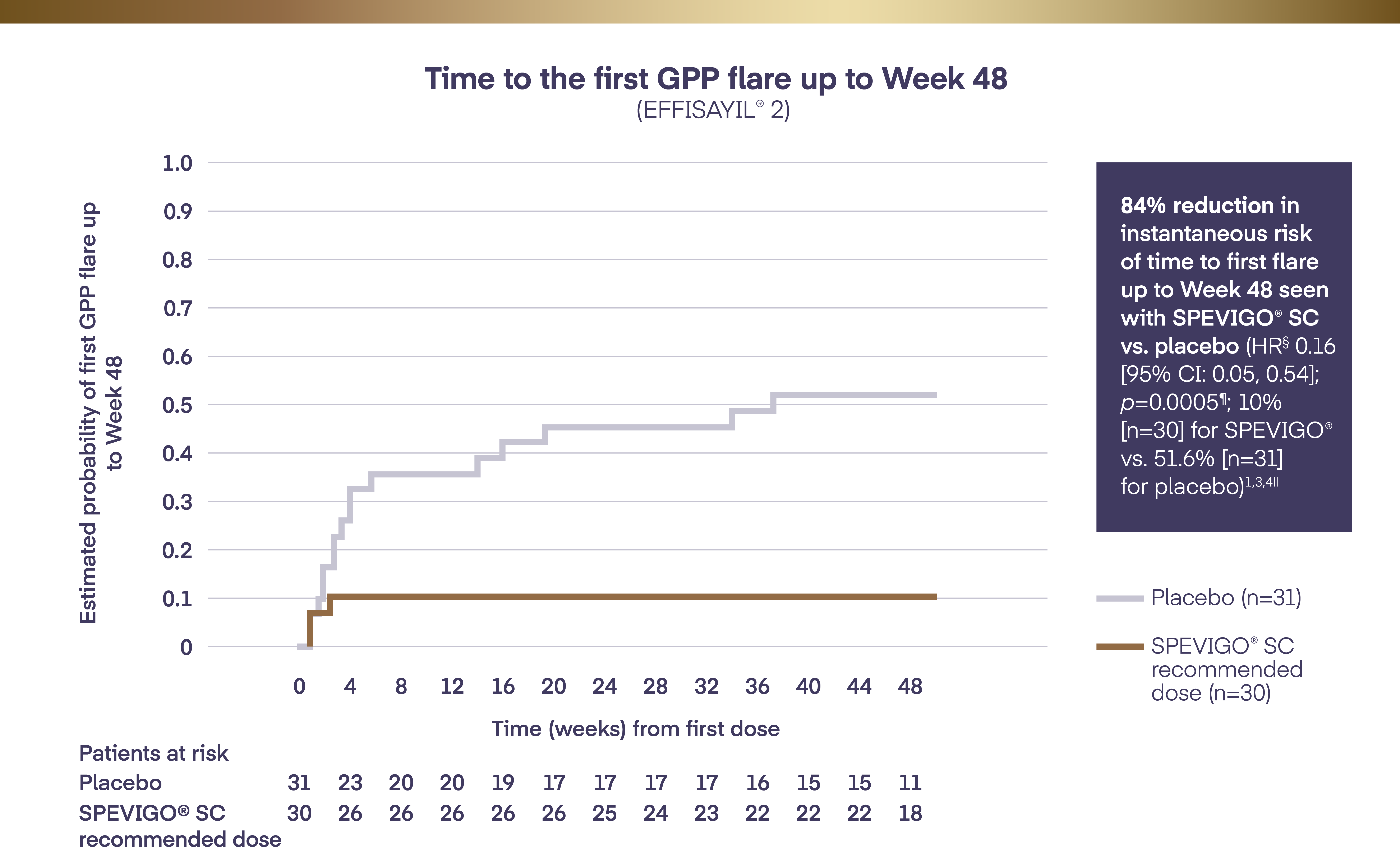
In the phase IIb clinical trial, EFFISAYIL® 2, the efficacy and safety of SPEVIGO® SC was assessed.
SPEVIGO® SC demonstrated efficacy in the primary and key secondary endpoints vs. placebo:‡
SPEVIGO® SC significantly delayed time to first GPP flare up to Week 48 vs. placebo (HR§ 0.16 [95% CI: 0.05, 0.54]; p=0.0005¶; 10% [n=30] for SPEVIGO® vs. 51.6% [n=31] for placebo)1,3,4||
Significantly fewer patients experienced ≥1 GPP flare up to Week 48 with SPEVIGO® SC vs. placebo: 10% (n=30) vs. 51.6% (n=31), respectively (adjusted RD -39.0% [95% CI: -62.1, -15.9]; p=0.0013**, key secondary endpoint)1,3,4||
EFFISAYIL® 1 DATA
With a single dose of SPEVIGO®, 54.3% (n=19) of patients achieved a GPPGA pustulation subscore of 0 (no visible pustules) at Week 1 vs. 5.6% (n=1) with placebo (p=0.0004)1*†

With a single dose of SPEVIGO® IV, 42.9% (n=15) of patients achieved a GPPGA total score of 0 or 1 at Week 1 vs. 11.1% (n=2) with placebo (p=0.0118)1*†


Image is of a SPEVIGO® patient. Used with permission.
EFFISAYIL® 2 DATA
SPEVIGO® SC demonstrated statistically significant superiority vs. placebo for time to first GPP flare up to Week 481,3||
Adapted from the Product Monograph.
The results of the primary endpoint were generally consistent across subgroups including sex, age, race, BMI, body weight, mutation status in IL36RN, concurrent plaque psoriasis, GPPGA total score at baseline, and irrespective of any systemic GPP treatment at randomization.
-
CI=confidence interval; HR=hazard ratio; IV=intravenous; q4w=every 4 weeks; RD=risk difference; SC=subcutaneous.
-
*
EFFISAYIL® 1: A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial in adults with flares of GPP. Patients were randomized if they had a flare of GPP of moderate-to-severe intensity, as defined by a GPPGA total score (which ranges from 0 [clear] to 4 [severe]) of at least 3 (moderate), presence of fresh pustules (new appearance or worsening of pustules), GPPGA pustulation subscore of at least 2 (mild) and at least 5% of body surface area (BSA) covered with erythema and the presence of pustules. Patients received a single intravenous dose of 900 mg SPEVIGO® (n=35) or placebo (n=18), with optional second dose at Day 8 (follow up to 12 weeks). Patients in EFFISAYIL® 1 could receive up to 2 doses of 900 mg SPEVIGO® IV. Primary endpoint was proportion of patients with a GPPGA pustulation subscore of 0 (indicating no visible pustules) at Week 1.
-
†
One-sided p-value.
-
‡
EFFISAYIL® 2: A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled phase IIb study in adults and adolescent patients (weighing at least 40 kg) with a history of at least two GPP flares of moderate-to-severe intensity in the past. Patients were randomized if they had a GPPGA total score of 0 or 1 at screening and randomization. These patients must have had a history of flaring while on concomitant treatment for GPP or a history of flaring upon dose reduction or discontinuation of these concomitant medications. While 3 dosing regimens were studied, the recommended dosing regimen for GPP flare prevention is a SC loading dose of 600 mg SPEVIGO® followed by 300 mg SC q4w. Patients who experienced a flare were eligible to receive up to two open-label, IV doses of SPEVIGO®. Primary endpoint was the time to the first GPP flare, up to Week 48 (defined by a GPPGA pustulation subscore of ≥2 and an increase in GPPGA total score by ≥2 from baseline). Key secondary endpoint of the study was the occurrence of at least one GPP flare up to Week 48.
-
§
Cox regression model stratified by the use of systemic GPP medications at randomization.
-
¶
Log-rank test stratified by the use of systemic GPP medications at randomization, one-sided p-value.
-
||
The use of IV SPEVIGO® treatment or investigator-prescribed standard of care to treat GPP worsening were considered as onset of GPP flare.
-
**
Cochran-Mantel-Haenszel test after multiple imputation, stratified by the use of systemic GPP medications at randomization, one-sided p-value.
-
††
SPEVIGO® patient, may not be representative of all patients. Individual results may vary.
-
‡‡
Patients in either treatment arm who still experienced flare symptoms at Week 1 were eligible to receive a single intravenous dose of open-label 900 mg SPEVIGO®, resulting in 12 patients (34%) in the SPEVIGO® arm receiving a second dose of SPEVIGO® and 15 patients (83%) in the placebo arm receiving one dose of SPEVIGO® on Day 8. In addition, 6 patients (4 SPEVIGO® arm; 2 placebo arm) received rescue treatment with a single 900 mg dose of intravenous SPEVIGO® for reoccurrence of a flare after Day 8.


